Match the following term with its correct description lymphocyte – Lymphocytes, a critical component of the immune system, play a pivotal role in recognizing and combating foreign invaders. These specialized cells, classified into T cells, B cells, and NK cells, exhibit distinct functions in orchestrating immune responses.
Delving into the intricacies of lymphocyte biology, we explore their role in immune disorders, clinical diagnostics, and the intricate mechanisms of antibody production and cell-mediated immunity.
Introduction: Match The Following Term With Its Correct Description Lymphocyte
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a critical role in the body’s immune system. They are responsible for recognizing and responding to foreign invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
There are three main types of lymphocytes: T cells, B cells, and NK cells. Each type has a specific function in the immune response.
Types of Lymphocytes
The different types of lymphocytes and their functions are summarized in the following table:
| Type of Lymphocyte | Function | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| T cells | Recognize and destroy infected cells | Express the T cell receptor (TCR) |
| B cells | Produce antibodies to neutralize antigens | Express the B cell receptor (BCR) |
| NK cells | Kill infected cells and tumor cells | Do not express TCR or BCR |
Role in Immune Response
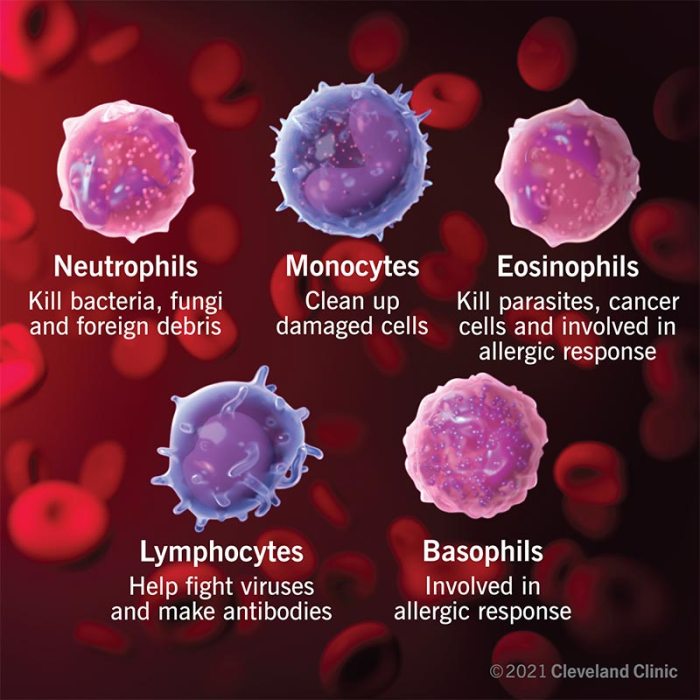
Lymphocytes play a critical role in the immune response. They are able to recognize and respond to antigens, which are foreign substances that trigger an immune response.
When an antigen is detected, it is presented to lymphocytes by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). APCs are cells that display antigens on their surface.
T cells recognize antigens presented by APCs and become activated. Activated T cells can then kill infected cells or help B cells produce antibodies.
B cells recognize antigens presented by APCs and become activated. Activated B cells can then produce antibodies, which are proteins that bind to and neutralize antigens.
Clinical Significance
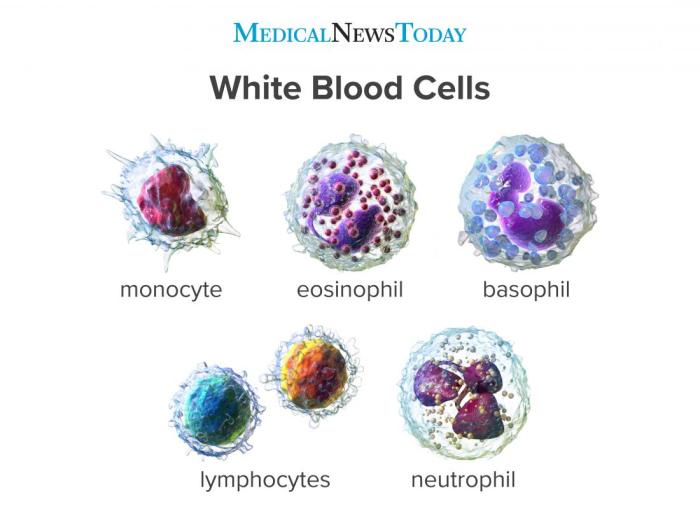
Lymphocytes play a role in a number of immune disorders, including autoimmune diseases and immunodeficiencies.
In autoimmune diseases, lymphocytes attack the body’s own tissues. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, depending on the specific autoimmune disease.
In immunodeficiencies, lymphocytes are not able to function properly. This can lead to an increased risk of infection.
Lymphocyte counts and function are used in clinical diagnostics to assess the immune status of patients.
Question Bank
What is the primary function of lymphocytes?
Lymphocytes are responsible for recognizing and responding to foreign antigens, orchestrating immune responses to protect the body from infection and disease.
How do T cells and B cells differ in their roles?
T cells primarily mediate cell-mediated immunity, directly targeting and eliminating infected cells, while B cells produce antibodies that neutralize pathogens and activate other immune components.
What is the clinical significance of lymphocyte counts?
Abnormal lymphocyte counts or function can indicate immune disorders, such as autoimmune diseases or immunodeficiencies, providing valuable diagnostic information.