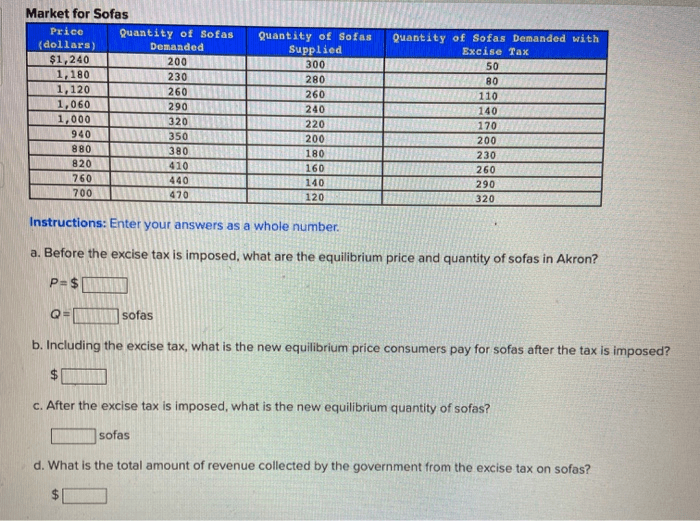
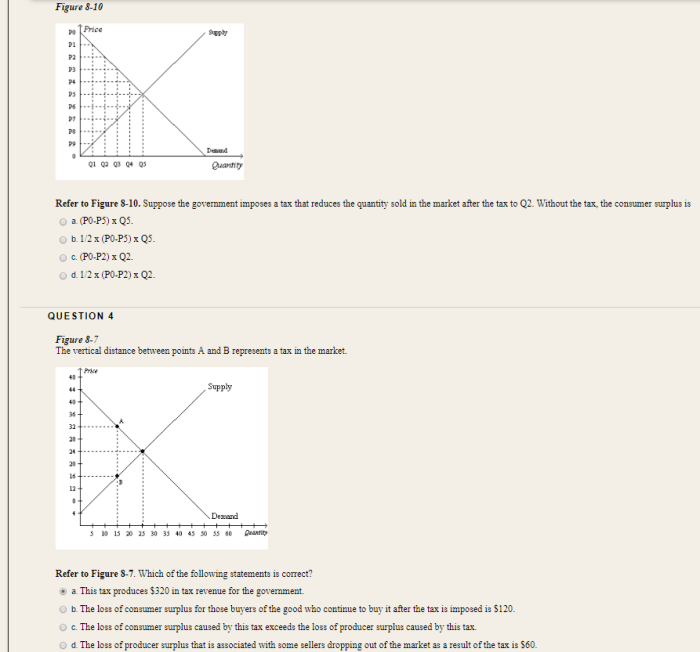
Assume the government imposes a tax on buyers – When the government imposes a $3 tax on buyers, it triggers a series of economic consequences that ripple through the market. This comprehensive analysis delves into the direct impact on consumer spending, the shifts in market equilibrium, the government revenue generated, and the potential policy alternatives.
By examining the incidence and efficiency implications of the tax, we gain a deeper understanding of its broader impact on consumers, producers, and the economy as a whole.
As we explore the complexities of this tax, we will uncover its effects on consumer surplus, market equilibrium price and quantity, and the distribution of the tax burden. Moreover, we will evaluate the effectiveness of alternative policy options in achieving desired policy goals.
Economic Impact on Consumers: Assume The Government Imposes A
Tax On Buyers
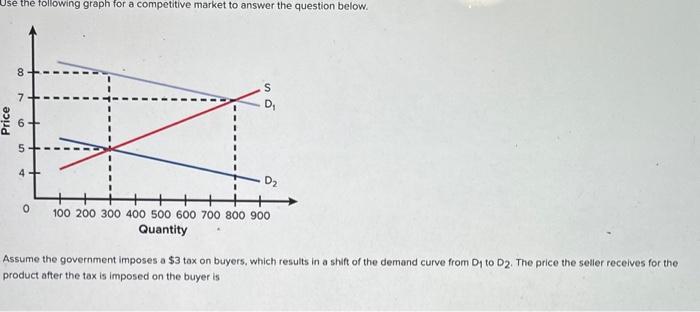
The imposition of a $3 tax on buyers will have a direct impact on consumer spending. The tax increases the price of goods and services, reducing the purchasing power of consumers. This can lead to a decrease in consumer surplus, which is the difference between the price consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and the actual price they pay.
The tax may also affect consumer behavior. Consumers may choose to purchase less of the taxed goods and services or switch to cheaper alternatives. This can lead to a decrease in demand for the taxed goods and services.
Impact on Market Equilibrium, Assume the government imposes a
tax on buyers
The tax will shift the supply and demand curves. The supply curve will shift to the left as producers pass on the cost of the tax to consumers. The demand curve will shift to the left as consumers reduce their purchases of the taxed goods and services.
The resulting changes in supply and demand will lead to a new market equilibrium price and quantity. The equilibrium price will increase, and the equilibrium quantity will decrease.
Government Revenue and Tax Incidence
The government will generate revenue from the tax. The amount of revenue will depend on the quantity of the taxed goods and services sold. The tax incidence refers to who ultimately bears the burden of the tax. In this case, the tax incidence will fall on both consumers and producers.
Alternative Policy Options
There are a number of alternative policy options that the government could consider instead of a tax. These options include subsidies, regulations, and public education campaigns.
| Policy Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Subsidies | Can encourage the production of desired goods and services, reduce consumer prices | Can be expensive, may lead to market distortions |
| Regulations | Can protect consumers from harmful products or practices, ensure quality standards | Can be burdensome for businesses, may stifle innovation |
| Public Education Campaigns | Can raise awareness about important issues, change consumer behavior | Can be difficult to measure effectiveness, may not be sufficient to achieve desired outcomes |
FAQ
What is the direct impact of the tax on consumer spending?
The tax directly reduces consumer spending by increasing the price of goods and services.
How does the tax affect consumer surplus?
The tax reduces consumer surplus by creating a wedge between the price consumers are willing to pay and the price they actually pay.
Who ultimately bears the burden of the tax?
The incidence of the tax depends on the elasticity of supply and demand. In general, consumers and producers share the burden of the tax.